Whether you’re new to SEO, or a seasoned manager, SEO terms can sometimes be hard to digest. The amount of terms that you deal with in any campaign is enough to hurt your brain.
We decided to create this handy guide for SEO newbs and SEO directors alike. And while this is a comprehensive list of the most common SEO terms, there are hundreds more that we aren’t hitting on. Hopefully, this can be a great starting point for you.
Feel free to click through the letters to get to the spot you’re most interested in learning about.
#
301 Redirect – a 301 redirect is used for a URL that has been moved permanently. These types of redirects pass roughly 90% of link equity. This is the most recommended redirect for SEO.
302 Redirect – a 302 redirect means that a URL was found and has been moved temporarily.
404 Redirect – a 404 error means page not found. This means that the page a browser was requesting isn’t found by the server.
410 – Redirect
A
Algorithm – complex data used by search engines to deliver results for a certain query. With a combination of algorithms, search engines are able to deliver ranked pages based on a number of signals and ranking factors.
Algorithm Updates – This is when search engines change certain signals and ranking factors for the current algorithm.
Alt Attribute – code that gives information to search engines and screen readers (accessibility for the visually impaired) to understand an image on your site.
Analytics -Analyzing and interpreting data to impact action in future strategies based on what has or hasn’t worked in the past. Learn more here.
Anchor text – Clickable word or phrases of a link, giving information to both people and search engines about what the website they’re clicking to is about.
Authority – Combo of signals search engines utilize to rank a website properly.
B
B2B – Business to Business. B2B SEO is the science of reaching professionals through search engines. It should answer 3 things: what are people looking for? How can we satisfy their needs? How do we convince Google that we can satisfy their needs?
Backlinks – Backlinks are inbound links that originate from someone elses’s website. If you link to Google, that’s a backlink for Google and vice versa. **Backlinks are one if the main signals in the algorithm right now to increase your rankings.
Black hat SEO – Going against Google Webmaster Guidelines. These are risky, spammy SEO tactics.
Bounce rate – The number of people who come to your website and leave without visiting another page. These depend widely on your industry, and although it’s not a direct ranking factor, it indicates website issues.
Broken link – a link (whether page or image) that leads to a 404 not found page. If you haven’t implemented a redirect (301), or if your website goes offline, this can create a 404.
C
Canonical – To reduce duplicate content, adding a canonical URL shows search engines which URL is the preferred page when multiple pages have similar (or the same) content.
CTR – Also known as click-through-rate, shows a percentage of users who click on an organic search result to visit your website. Calculated by dividing clicks by impression and multiplying by 100.
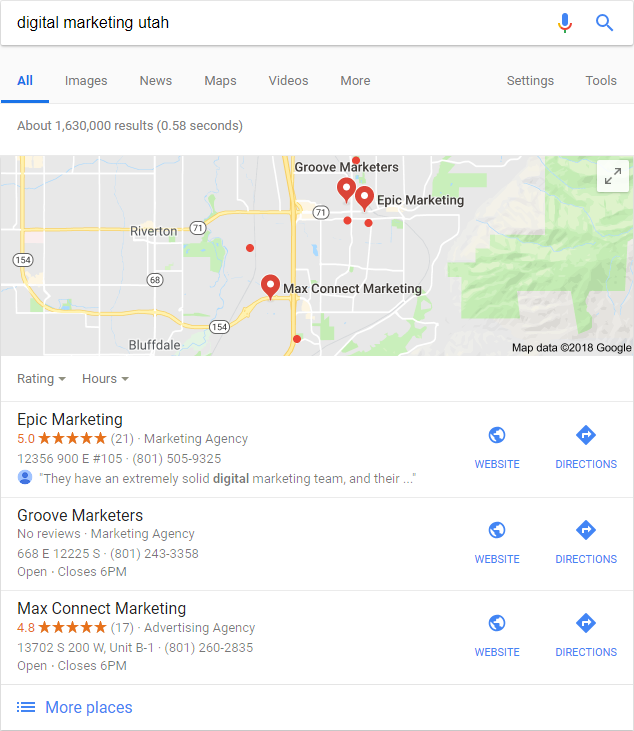
Citation – Also known as a local listing, citations are an online reference to your business name, address and phone number (NAP). Your NAP consistency plays a large role in your local relevance in search.
Competitor Analysis – When auditing a potential clients SEO efforts, look at competitors and what they’re doing that you aren’t doing and vice versa. There are SEO competitors (competing for the same keywords and search visibility) and direct competitors (companies that sell similar products and services to the same target audience).
Content – words, images, and videos that convey information to be consumed by your audience. Aside from link building, content is the most important ranking factor on Google. Search engines reward useful, informative and engaging content.
Conversion – this is an action completed by a user on your website like completing a purchase, downloading content, subscribing to a newsletter and filling out a contact form.
Conversion Rate – The rate that users complete a website action. Calculated by dividing the total number of conversions by traffic and multiplying by 100.
CRO – Optimizing opportunities for conversions on a website (homepage, landing pages, etc.).
Crawling – a program search engines to use crawl the web and more specifically, your website. Bots, spiders, and crawlers collect information and add it to a search engines index. The 3 types of crawling programs are:
• Google bots
• Crawler
• Spider
D
Directory – A list of websites in related categories that allows your website inclusion (free and paid). Slowly this type of link building isn’t as valuable as it used to be.
Disavow – If your website somehow gets hacked or includes a number of spammy and low-quality inbound links and can have negative harm on your rankings. You typically don’t have control over these links, but you can ask Google to ignore those links through their disavow tool.
Do-follow link – a link that passes link juice and doesn’t contain the nofollow attribute.
Domain Authority – Your strength and authority of your website, with a score between 0-100. It takes a lot of time to build up this “strength”, but it helps your rankings significantly.
Duplicate content – When more than one webpage contains similar if not the same content as one another (same website or completely different website).
E
Ecommerce – Buying and selling products online.
Editorial Link – Also known as a natural link, this is a link given by another website without you asking for it.
Engagement metrics – Ways to measure how users interact with your website. These include things like:
• CTR
• Conversion rate
• Bounce rate
• New vs. returning visitors
F
Featured Snippet – who/what/where/when/why/how query answers that Google shows in a block about the organic search results.
G
Google
• Analytics – Program to analyze and interpret data to impact action in future strategies based on what has or hasn’t worked in the past.
• Hummingbird – 2013 Google algorithm with a goal of understanding the context of queries instead of just keywords.
• Panda – 2011 Google algorithm update with a goal to reduce low-value content visibility.
• Penguin – 2012 Google algorithm update with a goal to reduce the visibility of overly-optimized sites, especially those with low-quality links and keyword stuffing.
• Pigeon – 2014 Google algorithm update with a goal to improve the relevance of local searches.
• Rankbrain – 2015 algorithm change that adds machine learning, the third most important ranking signal.
• Search Console – Program that helps you monitor your site for indexing errors and site speed.
• Trends – Google trends allows you to explore data for trends, stories, and topics.
• Posts – Google Posts is a feature that lets you include a post with your local listing to tell customers and potential customers about: Events, Products, Promotions/specials, Announcements.
• Tag Manager – A program that allows you to add tags and snippets of code to a website without the use of a programmer or web developer.
Guest Blogging – Link building tactic involving writing content for other websites in exchange for a backlink to your website.
H
Heading – Heading tags separate content into sections. H1 is the most important with H6 being the least important.
HTML – Hypertext Markup Language. Code elements used to improve SEO for websites.
HTTP/HTTPS – HTTP is how data is transferred from server to browser. HTTPS is the secure version of that. HTTPS is also a small ranking factor for Google.
I
Inbound links – Link pointing to one website from another website.
Index – A database that searches and retrieves information from a website to then use to match a user to the right query.
Internal link – Link from one page to another page within the same site.
IP address – IP stands for internet protocol. Every computer that’s connected to the internet has an individual, unique IP address.
J
Javascript – a programming language that can be embedded into HTML to add dynamic features to a webpage or site to make it more interactive.
K
Keyword
Cannibalization – In simple terms, it’s self-competition that happens when multiple pages on your site rank for the same query on the search engines. It can hurt your authority and lower your conversion rates.
Density – How many times a keyword/phrase appears in the content of a webpage. While there is no ideal percentage to help with rankings, it’s said to keep it between 2-3%.
Research – discovering relevant keywords to your focus SEO strategy. This can be done through research tools, analytics, competitor sites etc.
Stuffing – writing content that uses a keyword or phrase excessively.
Knowledge graph/panel – A box that appears at the top of the search results on relevant queries. Queries that have a quick, easy answer. These are things like song search, lyric search, recipe search, and celebrity searches.
KPI – Key performance indicators are ways to measure the results of your SEO strategies. These are things like the number of sessions, conversions, traffic, pages per session etc.
L
Local SEO – Local SEO targets potential customers within a specific geographic area. Optimizing content with localization, local listings etc.
Landing page – The first page a user lands on after clicking on a link from the search results.
Link building – Process of building high-quality backlinks that search engines use to evaluate the authority of your website.
Log file analysis – Assessing data kept in a log file to see trends, user movements through the site and understand how bots are crawling your site.
LSI – Latent Semantic Indexing is the keywords that are semantically related to the main keywords. You can see a list of LSI keywords for a keyword you use in a query at the bottom of the SERPs.
M
Metadata
• Description – the meta description is the sentence or two that shows up under the title of your website in the SERPs. Should be relevant, reinforce what the page is about and contain keywords or phrases.
• Title – the meta title, or title tag, needs to be unique to every page and describe what important ideas are covered in the content. Should keep between 8 and 10 words.
• Keywords – meta keywords is a tag that is used to highlight keywords or phrases that the page is targeting.
Metric – a way to measure the performance of campaign to see if it’s successful or not.
N
Negative SEO – an extremely harmful practice where webspam techniques are used to hurt a competitor.
Niche – Small group of people in a specific market or industry.
No follow/no index – a tag that tells search engines not to follow a specific external link or index a specific page in the index.
O
Off-page SEO – SEO strategies done outside of the website including: social media marketing, email marketing, influencer marketing etc.
On-page SEO – strategies put in place inside the website including optimizing images, metadata, content etc.
Organic search – the unpaid listings that appear in the SERPs, typically underneath the ads at the top. These results are analyzed and ranked by the algorithms and shown in the results based on a specific, related query.
Outbound link – a link that directs your website visitors to a different page on a different website.
P
Pagerank – PageRank measures the importance of a page based on backlinks to it. Each QUALITY link adds to your PageRank.
Page speed – The amount of time it takes for a website or page to load completely and is a big ranking factor.
Paid search – advertisements that appear above the organic search results.
Penalty – Search engines penalize websites for spammy tactics. This penalty prevents these spammed sites from ranking high in the results.
Pogo-sticking – When a user bounces back and forth between a SERP and the pages listed.
Q
Query – the phrase or keyword that users enter into a search engine.
Quality content – Content that helps you achieve your SEO goals of high rankings that generate leads or sales.
Quality link – A backlink that comes from an extremely authoritative, relevant website.
R
Robot.txt – a text file that tells search engines which areas of a website should be crawled and ignored.
Ranking – where, in the SERPs, your website appears in the organic search results for a certain query.
Reciprocal links – when two different websites have an agreement to exchange links with one another.
Redirect – a way to let search engines know that the location of a page moved. Users will then be directed to a new, but a relevant webpage.
Responsive website – a website that automatically adjusts to the size of someone’s smart device.
Rich snippet – structured data added to a website that provides additional context to a certain webpage to enhance a listing.
S
Schema – structured data or microdata that gives more context to search engines and helps show the positive tactics like positive reviews, events, products, location etc.
Search engine – a program that allows users to search queries and find answers and relevant information. Here’s a list of the most common search engines:
• Google
• Yahoo
• Baidu
• Yandex
• DuckDuckGo
• Bing
SEM – a term describing visibility in search engines that includes both paid and organic strategies.
SEO – making a business appeal to both users and search engines with a combination of technical and on-page marketing.
SERP – the page on search engines that displays after a user conducts a search query.
Sitemap – a way for crawlers and bots to navigate your website.
Status codes – response codes sent to a server after a link is clicked. Common codes are:
• 200
• 301
• 302
• 404
• 410
• 500
• 503
T
TLD (top-level domain) – end of a given web address. Like
• .com
• .org
• .net
Traffic – users and crawlers who visit your website.
U
URL – the web address entered into a browser to go to a webpage.
URL parameter – an added piece to a URL that tracks where traffic comes from like: facebook, twitter, google listing etc.
User Experience – the feeling users are left with after being on your website and interacting with your online presence.
V
Voice search – voice search requires you to use your voice to ask questions and conduct online search queries through smart devices.
W
Website navigation – How websites help users navigate through the site. There are a few different ways to implement navigation:
• Main
• Footer
• Breadcrumbs
White hat SEO – SEO tactics that specifically comply with Google Webmaster Guidelines.
Word count – The number of words that appear within your content. Low word count can signal search engines of a low-quality website.
WordPress – a popular website management/creation software platform.
X
XML Sitemap – a text format sitemap that search engines can read.
Y
Youtube – Second largest search engine that usually ends up with more search traffic than Yahoo and Bing combined.
Hopefully, this list helped you learn something or help you figure out an issue you were having with one of your campaigns. If we’re missing any super important terms that you use on a regular basis, let us know and we’ll get it added!